General information
The impeller used on a mixer is the most important component of all. It is the type of impeller, its size and rotational speed that determines the specifications of every other component of the mixer. Further, there is no particular impeller type that performs all mixing tasks adequately.
There are a great number of different impellers and the selection of the correct mixer for the duty is essential to the performance of your production line. Below are some examples the more common types of impellers and turbines typically used in industry.
H3000 – Description: Axial flow impeller producing high flow for a relatively low power.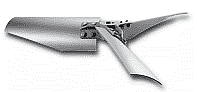
Applications: – Low viscosity blending, heat transfer, storage tanks and silos and solids suspension.
Click here to find out about Static Mixers
H5000 – Description: High solidity impeller producing high flow for moderate power.
Applications: – Medium to high viscosity blending and gassing applications.
T4450 – Description: Relatively high power consumption when used in medium to high viscosity ranges. Imparts medium levels of shear.
Applications: – Medium to high viscosity blending and low level mixing.
T4490 – Description: High specific power consumption.
Applications: – Low level mixing.
Click here to find out about mixer drives
Hi gh shear impeller – Description: Multi tipped impeller used at high peripheral speeds. Imparts high levels of shear.
gh shear impeller – Description: Multi tipped impeller used at high peripheral speeds. Imparts high levels of shear.
Applications: – Used for solids dispersion typically in the paint and ink industries.
Specials
A number of less common impeller types are found in more specific applications for example emulsifiers, anchor and spiral impellers for high viscosity products, retreat blade turbines and gate type flocculator impellers.